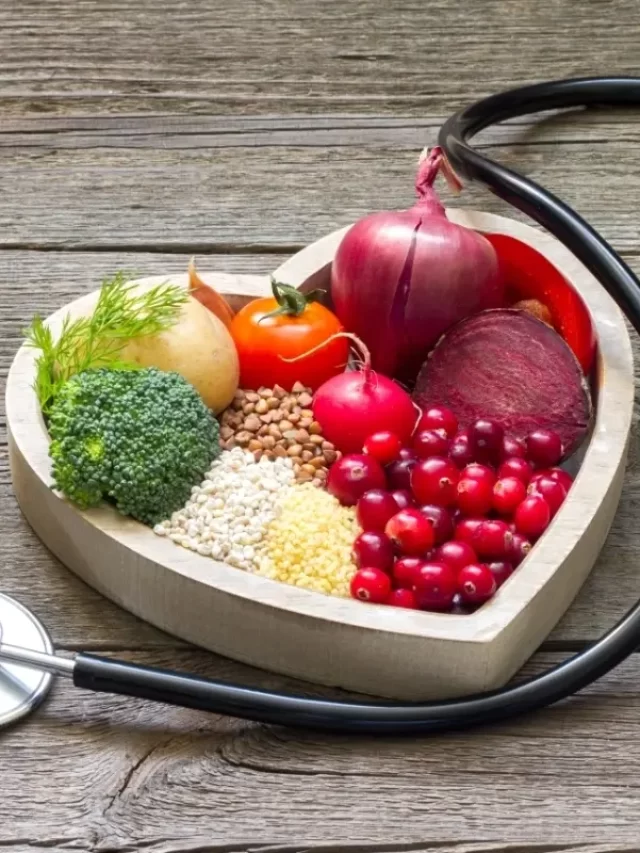
Blood sugar levels and their connection to the food we consume. In this article, we’re delving into the dynamic interplay between what we eat and how it influences our blood sugar regulation. Keeping our blood sugar levels steady is essential for overall health, as it affects our energy, mood, and even weight management. Join us as we unravel the significance of maintaining balanced blood sugar levels and explore practical insights for a healthier lifestyle.
🔍 Why Stable Blood Sugar Matters:
- Sustained energy levels
- Enhanced mood and focus
- Weight management support
Let’s embark on this journey to understand how our food choices can either help or hinder our blood sugar control, and learn simple yet impactful ways to make more informed dietary decisions.
Let’s dive into the essential foods that play a pivotal role in regulating blood sugar levels. What are the core food categories that individuals mindful of their blood sugar should concentrate on?
🥦 Fiber-Rich Gems: Incorporate these foods to slow down sugar absorption.
- Whole grains: oats, quinoa, brown rice
- Fresh vegetables: broccoli, spinach, carrots
🍓 Vibrant Fruits: Opt for those with lower glycemic index (GI) values.
- Berries: blueberries, strawberries, raspberries
- Citrus fruits: oranges, grapefruits
🥑 Healthy Fats: They aid in managing blood sugar spikes.
- Avocados
- Nuts and seeds: almonds, chia seeds
🍳 Lean Proteins: Assist in stabilizing blood sugar levels.
- Chicken or turkey breast
- Fish: salmon, tuna
By focusing on these foundational food groups, you can proactively contribute to better blood sugar control and overall health. It’s about making choices that positively impact your body’s balance.
Complex carbohydrates play a pivotal role in influencing blood sugar levels. These carbs are made up of longer chains of sugar molecules, which take more time for your body to break down and digest compared to simple carbohydrates. This gradual digestion leads to a slower and steadier release of glucose (sugar) into the bloodstream, which is highly beneficial for blood sugar control. Here’s how complex carbs work:
🌾 Complex Carbohydrates and Blood Sugar:
- Slower Digestion: Foods rich in complex carbs, like whole grains, legumes, and vegetables, contain fiber and starches that require more time to break down. This gradual process leads to a gentler rise in blood sugar levels.
- Steady Energy: The slow release of glucose provides a sustained supply of energy, preventing rapid spikes and crashes in blood sugar. This is particularly important for maintaining consistent energy levels throughout the day.
- Fullness and Satiety: Complex carbs often come with a good amount of fiber, which adds bulk to your meals and promotes a feeling of fullness. This can help prevent overeating and support weight management.
- GI Index: The Glycemic Index (GI) measures how quickly a food raises blood sugar levels. Complex carbs generally have a lower GI compared to simple carbs, meaning they have a milder impact on blood sugar.
🍽️ Incorporating Complex Carbs:
- Opt for whole grains like brown rice, quinoa, whole wheat bread, and oats.
- Include legumes such as lentils, beans, and chickpeas in your meals.
- Load up on colorful vegetables like sweet potatoes, broccoli, and spinach.
By focusing on complex carbohydrates, you can enjoy a more stable and balanced blood sugar response while nourishing your body with essential nutrients and energy.
Lean proteins play a crucial role in managing blood sugar levels by providing sustained energy and helping to control spikes in glucose. Here’s how they contribute to blood sugar management:
🍗 Lean Proteins and Blood Sugar Control:
- Slow Digestion: Lean protein sources, such as poultry, fish, and plant-based proteins like tofu, are digested more slowly compared to high-carb foods. This gradual digestion helps prevent rapid spikes in blood sugar levels.
- Stable Energy: Proteins provide a steady release of energy over a longer period. This can help maintain consistent energy levels and reduce the likelihood of experiencing energy crashes.
- Glucagon Regulation: Protein intake triggers the release of glucagon, a hormone that opposes the effects of insulin. This can help regulate the balance of glucose in the bloodstream.
- Satiety: Protein-rich foods tend to be more filling and satisfying, which can curb excessive hunger and prevent overeating. This is beneficial for weight management and blood sugar stability.
🍽️ Incorporating Lean Proteins:
- Choose lean cuts of meat such as skinless poultry and lean cuts of beef or pork.
- Include fatty fish like salmon, mackerel, and trout, which provide heart-healthy omega-3 fatty acids.
- Explore plant-based protein sources like lentils, beans, chickpeas, tofu, and tempeh.
By incorporating lean proteins into your diet, you can support your blood sugar management goals while enjoying a variety of nutrient-rich and satisfying foods.
let’s dive into the role of healthy fats in supporting blood sugar control:
🥑 Healthy Fats and Blood Sugar Balance:
- Slow Digestion: Healthy fats, such as those found in avocados, nuts, seeds, and olive oil, slow down the digestion of food. This can lead to a more gradual release of glucose into the bloodstream, helping to avoid sudden spikes.
- Insulin Sensitivity: Some healthy fats, particularly omega-3 fatty acids found in fatty fish, flaxseeds, and walnuts, may improve insulin sensitivity. This means your body can use insulin more effectively to regulate blood sugar.
- Satiety and Cravings: Fats are more calorie-dense and can contribute to feelings of fullness and satisfaction. Including healthy fats in your meals can help control cravings and overeating, indirectly supporting blood sugar management.
- Balanced Meals: Combining healthy fats with carbohydrates and proteins in your meals can create a balanced nutritional profile. This combination can lead to slower digestion, more stable blood sugar levels, and sustained energy.
🍽️ Incorporating Healthy Fats:
- Use olive oil or avocado oil for cooking and dressing salads.
- Snack on a handful of nuts (e.g., almonds, walnuts) or seeds (e.g., chia, flaxseeds).
- Include avocados in salads, sandwiches, or as a creamy spread.
Remember, while healthy fats are beneficial, moderation is key due to their higher calorie content. Including a variety of sources can add both flavor and health benefits to your meals while assisting in blood sugar control.
carbohydrates are a crucial source of energy for our bodies, and it’s important to approach the topic of carbohydrates and blood sugar control with nuance. While some individuals may argue for avoiding all carbohydrates to control blood sugar, it’s essential to consider the role carbohydrates play in providing energy and supporting overall health.
🍞 Balancing Carbohydrates for Blood Sugar Control:
- Complex vs. Simple Carbs: Instead of avoiding all carbohydrates, focus on differentiating between complex and simple carbs. Complex carbs, found in whole grains, vegetables, and legumes, are generally better for blood sugar control due to their slower digestion and gradual impact on glucose levels.
- Portion Control: Managing portion sizes is key. Overeating any type of carbohydrate can lead to blood sugar spikes. Moderation is important to prevent excess glucose from entering the bloodstream at once.
- Nutrient Value: Many carbohydrate-rich foods are rich in essential nutrients and fiber, both of which are beneficial for overall health. Whole grains, for instance, provide vitamins, minerals, and dietary fiber that contribute to well-being.
- Energy Balance: Carbohydrates are a primary energy source for our bodies. Cutting them out entirely can lead to low energy levels, fatigue, and potential nutrient deficiencies.
In essence, rather than avoiding carbohydrates altogether, the focus should be on making informed choices about the types of carbohydrates you consume and their portion sizes. Balancing your diet with complex carbs, lean proteins, healthy fats, and plenty of vegetables can contribute to stable blood sugar levels while providing the energy your body needs to function optimally. It’s about finding the right balance for your individual needs and health goals.
Here are a few examples of meals that incorporate blood sugar-stabilizing foods:

Breakfast:
- Oatmeal topped with sliced strawberries and a sprinkle of chopped nuts.
- Whole grain toast with avocado spread and a poached egg.
- Greek yogurt parfait with mixed berries and a drizzle of honey.
Lunch:
- Grilled chicken salad with mixed greens, cherry tomatoes, cucumber, and a vinaigrette made with olive oil and balsamic vinegar.
- Quinoa and black bean bowl with roasted vegetables, salsa, and a dollop of guacamole.
- Whole wheat wrap filled with lean turkey, hummus, spinach, and shredded carrots.
Dinner:
- Baked salmon with quinoa and steamed broccoli.
- Stir-fried tofu with a variety of colorful vegetables in a sesame ginger sauce, served over brown rice.
- Grilled lean steak with roasted sweet potatoes and a side salad.
let’s recap the key foods that individuals should prioritize in their diet to effectively manage their blood sugar levels:
Complex Carbohydrates:
- Opt for whole grains like oats, quinoa, and brown rice.
- Include fiber-rich vegetables such as broccoli, spinach, and carrots.
Lean Proteins:
- Choose sources like skinless poultry, fish, tofu, and legumes.
- Incorporate protein to support stable blood sugar levels and sustained energy.
Healthy Fats:
- Use olive oil, avocado oil, and consume avocados.
- Enjoy nuts, seeds, and fatty fish to help control blood sugar spikes.
Colorful Fruits:
- Select fruits with a lower glycemic index, such as berries and citrus fruits.
- Enjoy the natural sweetness of fruits while managing blood sugar impact.
Balanced Meals:
- Create balanced meals that include a combination of complex carbs, lean proteins, healthy fats, and vegetables.
- Portion control and variety are key to maintaining stable blood sugar levels.
By incorporating these foods into your daily meals, you can take proactive steps toward managing your blood sugar levels effectively while enjoying a diverse and nutritious diet. Remember that individual needs may vary, so it’s a good idea to work with a healthcare professional or registered dietitian to tailor your dietary choices to your unique health goals and requirements.
ALSO READ:
Taking Charge of My Health Journey: Taming High Blood Sugar After 40
Fruits to Avoid: The Surprising Truth about Fruits That Raise Blood Sugar Levels
How To Lower Your Blood Pressure Naturally – A Home Remedy Guide
Eating onions can help diabetics control their blood sugar levels; learn how they should eat onions.